Cloud Computing vs. Edge Computing: Which One is Right for Your Business?
In today’s fast-paced digital economy, businesses rely on technology not just to stay competitive but to innovate, adapt, and grow. One of the most important decisions modern businesses face is how to manage and process data efficiently. With the explosion of data from IoT devices, mobile apps, and enterprise systems, two technologies have emerged as key solutions: Cloud Computing and Edge Computing. Each approach has its advantages and trade-offs, and choosing the right one depends largely on your business needs, infrastructure, and goals.
What is Cloud Computing?
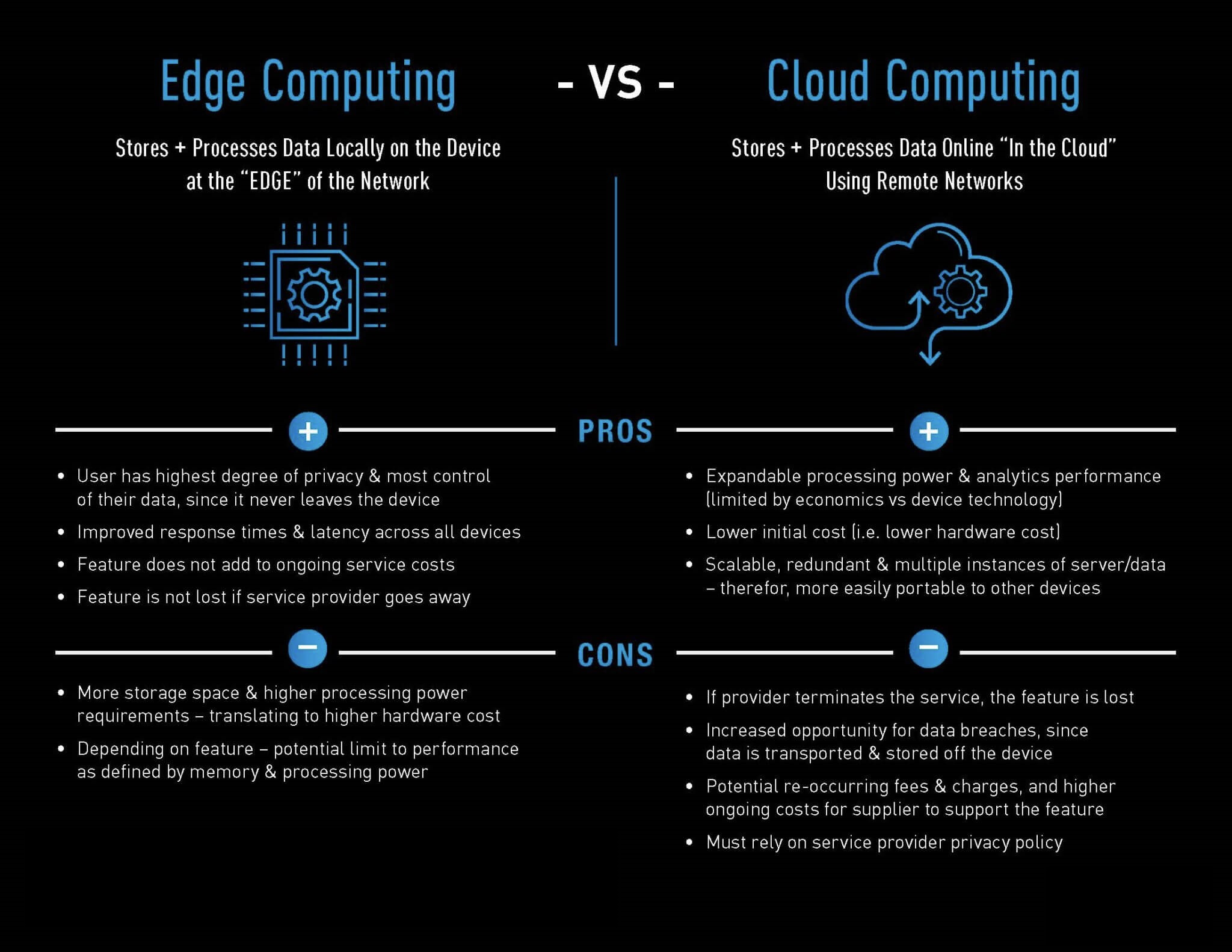
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including storage, processing power, databases, networking, and software—over the internet, often hosted by third-party providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud. Instead of maintaining physical servers or data centers, businesses can access resources on demand, scale up or down easily, and only pay for what they use.
The benefits of cloud computing are numerous. It enables cost savings, supports global accessibility, and provides robust security, automatic updates, and disaster recovery options. It’s ideal for businesses focused on agility and scalability.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the physical location where it is generated—at the “edge” of the network. Instead of sending all data to a centralized cloud server, edge computing processes data locally, often on IoT devices, gateways, or local servers.
This approach reduces latency, improves response times, and minimizes bandwidth usage. It’s essential for applications that require real-time decision-making, such as autonomous vehicles, smart factories, and remote healthcare. Edge computing is about speed, reliability, and local control.
Key Differences Between Cloud and Edge Computing
- Latency: Cloud introduces more latency; edge is optimized for low-latency use cases.
- Bandwidth: Cloud can consume more bandwidth; edge reduces data transmission.
- Scalability: Cloud offers massive scalability; edge has hardware limitations.
- Security: Cloud has centralized security; edge offers more localized data privacy.
- Cost: Cloud is cost-effective for scalable operations; edge may have higher initial costs.
When Should You Choose Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is ideal for businesses that:
- Need to scale quickly without upfront hardware costs.
- Have distributed or remote teams.
- Rely on SaaS platforms and cloud-native apps.
- Require centralized data and security management.
- Are focused on analytics, data storage, and collaboration tools.
When Should You Choose Edge Computing?
Edge computing is right for businesses that:
- Need real-time processing and low-latency operations.
- Operate in remote or bandwidth-constrained environments.
- Use IoT devices in manufacturing, logistics, or healthcare.
- Want to reduce cloud bandwidth costs and enhance data privacy.
- Have time-sensitive applications like AR, robotics, or surveillance.
Can You Use Both? A Hybrid Approach
Many businesses are embracing a hybrid model that combines both cloud and edge computing. For example, edge devices can process critical data locally in real time and then send summarized or non-urgent data to the cloud for storage and advanced analytics. This approach ensures businesses maintain performance and responsiveness while benefiting from cloud scalability and flexibility.
Conclusion
Cloud and edge computing are not mutually exclusive but rather complementary. Cloud computing offers scale, accessibility, and centralized management, while edge computing enables rapid, real-time insights and operational efficiency. By evaluating your business goals, data processing needs, and infrastructure, you can determine whether cloud, edge, or a hybrid solution is the best fit. In many cases, combining the strengths of both technologies is the smartest path forward.


